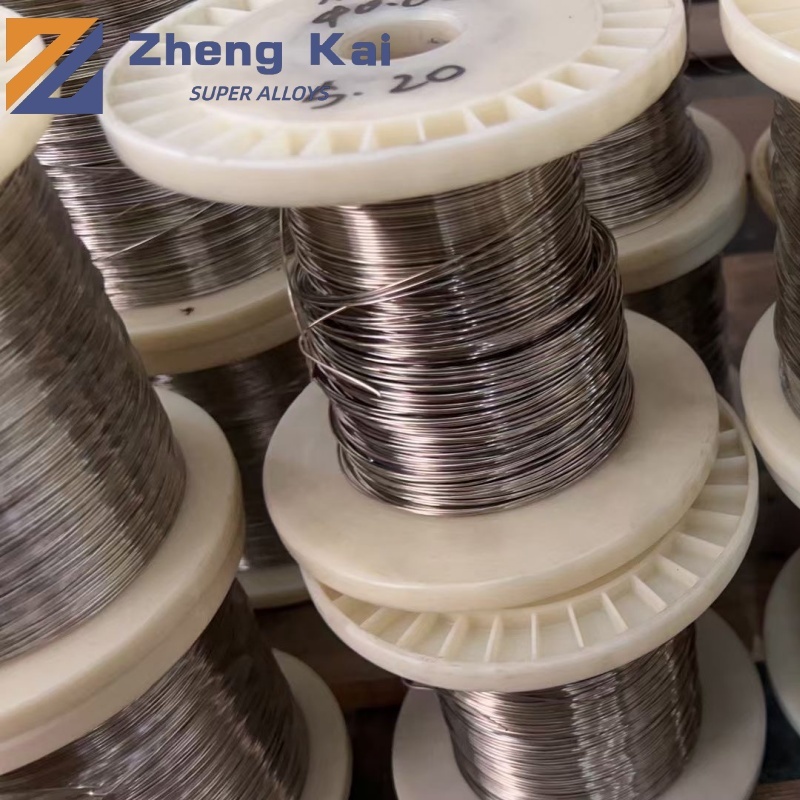
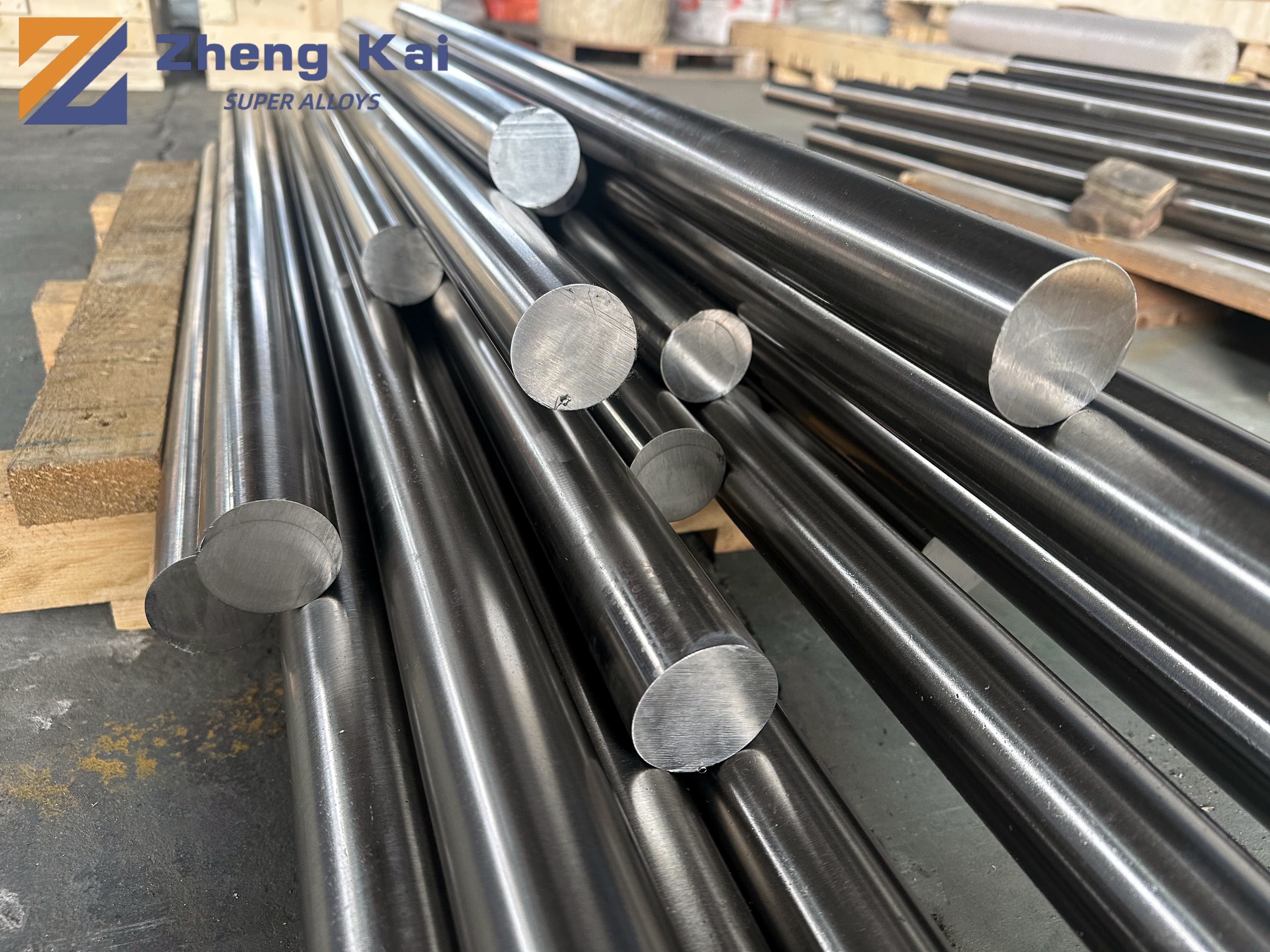
Alloy 42(UNS K94100)
Category: PRECISION ALLOYS
Alloy 42, also known as Invar 42 or FeNi42, is a nickel-iron alloy that is primarily composed of approximately 58% iron and 42% nickel. It is known for its low thermal expansion coefficient, which makes it particularly useful in applications requiring dimensional stability over a range of temperatures.
| Ni | Cr | Co
| Fe | C | Mn | S | Si | P |
MIN | 41.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAX | 42.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | balance | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 0.02 |
Physical Properties
Density | 8.11g/cm3
|
Melting Range | 1435℃
|
AVAILABLE PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS
Wire | ASTM F 29 |
Sheet, strip, rod, bar, tubing and wire | ASTM F30 |
Sheet and strip | ASTM B 753 |
Sheet, strip and bar | SEW 385 |
Features
Low Thermal Expansion: Alloy 42 has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications where precise dimensional stability is critical.
Magnetic Properties: It exhibits good magnetic properties, which can be advantageous in certain electromagnetic applications.
Good Machinability: Alloy 42 can be easily machined and formed, allowing for versatile applications in manufacturing.
Corrosion Resistance: While not as corrosion-resistant as some stainless steels, it still offers decent resistance in certain environments.
Applications:
- Precision Instruments: Used in the manufacturing of measuring instruments and devices that require high accuracy.
- Electronics: Employed in components where thermal stability is essential, such as in electronic housings and connectors.
- Aerospace and Defense: Utilized in various aerospace applications where dimensional stability is critical under temperature changes.
Advantages
- Dimensional Stability: Offers excellent dimensional stability across a wide temperature range, making it ideal for applications requiring high precision.
- High Efficiency: In applications like motors and transformers, Alloy 42 can help reduce size and weight while maintaining performance.
- Versatility: Its combination of magnetic and thermal properties makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
Limitations
- Electrical Resistivity: With a low resistivity (around 0.27 μΩ·m), it may not be suitable for high-frequency applications where higher resistivity is preferred.
- Cost: The cost of nickel can make this alloy more expensive compared to other materials, which may be a consideration for large-scale applications.
Keywords: Alloy 42(UNS K94100)
Previous page
Next page
Inquire Now
Note: Please leave your email address, our professionals will contact you as soon as possible!